NaOH or caustic soda has a wide application in various industries, including textiles, pharma, dairy, and food processing. In production systems, it is used from cleaning-in-place (CIP) systems to fabric treatment showers. This is done for sanitation and production quality control. However, this process yields large amounts of waste and expenses. At this point in time, caustic soda recovery comes into play.
A well-planned NaOH recovery system assists industries in transitioning towards more sustainable practices. At the same time, it reduces costs and improves operational efficiency. In this article, we’ll look at recovery systems and their sustainability roles for supportable plant operations.
What Is Caustic Soda Recovery?
The process of getting back valuable NaOH from used or spent caustic solutions is termed caustic soda recovery. These spent solutions are generated from processes like CIP in the food and pharma industries. These effluents can
be processed to recover and reuse caustic soda through:
- Membrane-based concentration (best for streams under 1–2% NaOH);
- Evaporation (tailored for stronger streams in the 5–12% NaOH range);
- Ion-exchange units (more for final polishing than for bulk NaOH recovery).
Using these chemical recovery systems, a plant can reclaim 80–90% of the initial caustic in a way that is both sustainable and cost-effective.
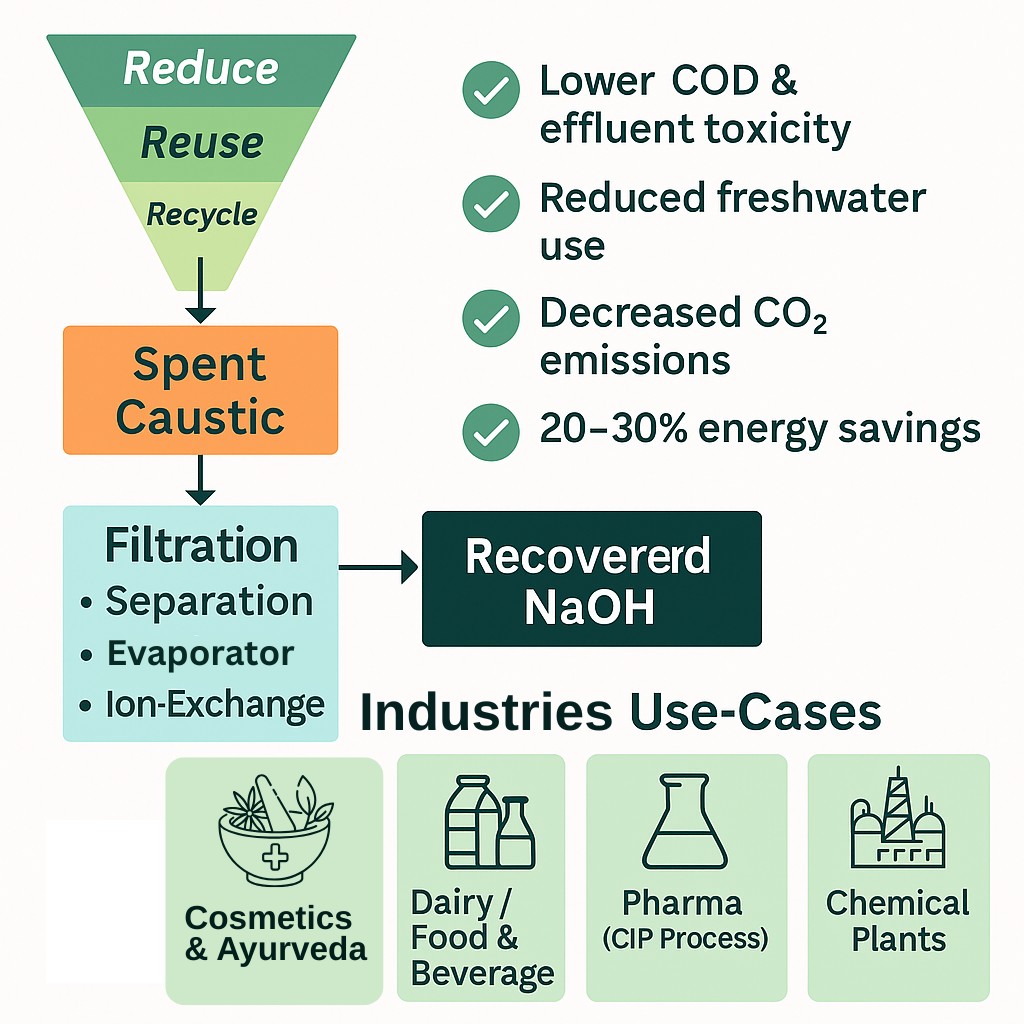
Environmental And Operational Advantages
The savings of caustic soda recovery go beyond its economic benefits. It’s also a move towards greener production. Recovery through recycling brings positive operational results. For example:
- Decreased chemical waste effluent: Using recycled caustic lowers the COD and alkalinity, which eases the treatment burden and curbing aquatic toxicity.
- Reduction of fresh water consumption: The availability of NaOH reduces the need for fresh chemicals, reducing water consumption.
- Reduction of CO₂ emissions: The caustic soda is produced with high energy. This results in decreasing emissions when NaOH is reused into the production process.
Implementing recovery systems underpins India’s ambition of achieving Zero Liquid Discharge and meets Central Pollution Control Board guidelines. A mid-sized dairy plant can retrieve per day spent caustic in high quantity, yielding a direct replacement of 5,000 to 10,000 litres of freshwater. This also lowers energy demand, carbon emissions, and related operational expenses by 20 to 30 %.
Such operational results speak directly to the nation’s expanding commitment to industrial ecological balance, to meeting statutory requirements, and to the effective application of compliance instruments.
Use-Cases In Industry
The scenarios for industrial application of the recovery of caustic soda are numerous:
- Mercerization and washing processes in the textile industry.
- Reclaiming CIP solutions in dairy, breweries, and soft drink production in the food and beverage industry.
- Recovery in the CIP caustic recovery units in pharmaceutical plants to ensure Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance.
- Chemical manufacturers are reusing caustic in closed-loop systems to minimize operational cost.
Such capabilities create significant value for industrial caustic recovery systems across multiple sectors.
Technical Components & Process Stages
To ensure an effective and safe retrial of spent caustic, a digestate recovery plant has multiple processes.
Storage & Collection Tanks
A stable supply is needed by the recovery system; therefore, spent caustic is collected in tanks.
Pre-Filtration
Fine filters and settling techniques capture sludge, suspended solids, and other organic constituents.
Separation Technology
- Selective ion separation in low-concentration streams can utilize membrane separation units.
- Evaporator systems are best suited for recovering high-concentration solutions like those in the textile industry.
There are some new developments in recovery systems using hybrid membrane filtration followed by evaporation to increase recovery and efficiency. These systems are becoming popular in plants that prioritize high-purity recovery at low energy expenditure.
To enable and ease the reapplication of the solution in cleaning and processing, every unit is designed to protect the recovered solution’s quality and safety.
How Sanitech Engineers Make it Sustainable?
In the recovery of caustic soda, Sanitech engineers are known for their reliable product in India. These systems are implanted with energetic and site-specific modular components configured to fit the location. Key features include:
- High-purity recovery through membrane-based caustic soda recovery.
- Reduced water footprint through integration with effluent treatment and caustic reuse systems.
- Low manual intervention coupled with high automation for better safety improves the overall process.
- Easy incorporation into pre-existing industrial infrastructures is made possible with a compact design.
Sanitech recovery systems are applied widely within the food and pharmaceutical industries, textile industries, and the chemical manufacturing industry.
Conclusion
Environmentally and financially beneficial, caustic recovery plants are an excellent option for India’s continued push towards sustainable industrial development. The eco-efficient caustic recycling process is an intelligent option and a responsible environmental choice due to its low chemical effluent discharge, water conservation, and resource optimization.
Your facility’s operational and maintenance costs can be optimized by enhanced sustainability, so look into caustic sodium recovery systems specifically designed for your industry.
Take advantage of the smartest options on the market today from companies like Sanitech and make your first step toward a chemically lean recovery system investment for a sustainable future.
FAQs
The main job of a caustic recovery plant is to extract pure sodium hydroxide from spent solutions. This cuts both the need for fresh chemicals and the overall operating costs.
Yes, it has wide applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries, particularly in CIP systems used in dairy and beverage plants.
Absolutely. By lowering wastewater volume, curtailing chemical discharge, and trimming carbon emissions, caustic recovery makes a plant’s operations significantly more sustainable.

