Membrane Systems
Microfiltration System
Sanitech Engineers is a leading microfiltration membrane systems provider, delivering high-performance solutions aligned with strict global regulatory standards.
Microfiltration (MF) is one of the very effective physical separation process for removing impurities, soft particles, turbidity and microbial biomass from fluid streams. The microfiltration membrane system uses membrane filters that are surface filters with precise micro-porous structure allowing smaller particles to pass through while retaining larger contaminants.
The widespread adoption of microfiltration system across industries including food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, dairy, and biotechnology stems from its reliability and cost-effectiveness in clarifying fluids and removing suspended solids.
We not only lead the field in microfiltration membrane solutions, but also offer advanced ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis systems engineered for precision and performance across industries.

Understanding Microfiltration: Working Principle and Types
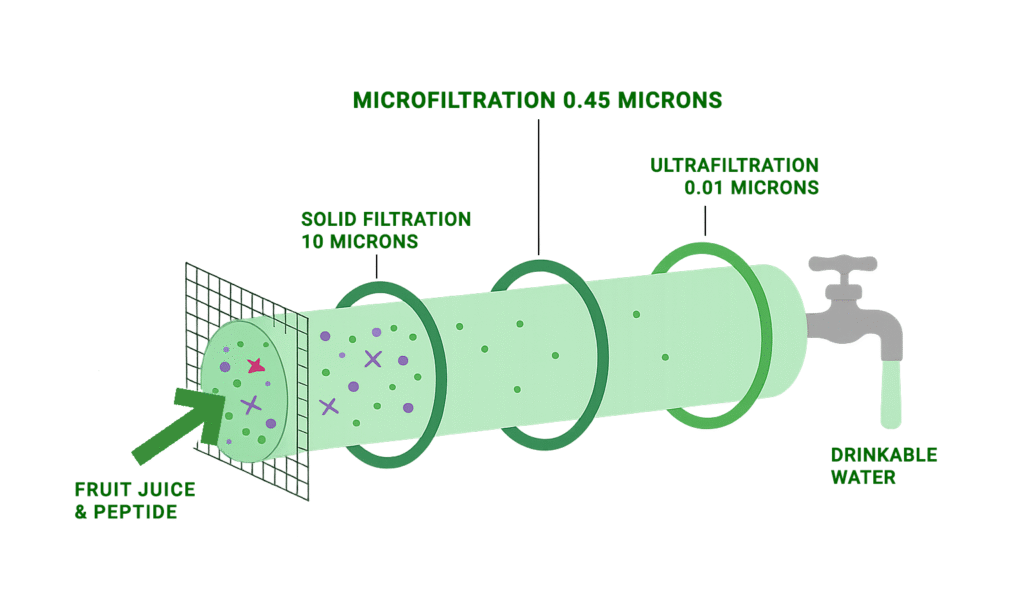
Microfiltration (MF) is a pressure-driven membrane separation process designed to remove suspended particles, colloids, and microorganisms while allowing dissolved salts and small molecules to pass through. It provides reliable clarification and sterilization for industries where product purity and consistency are critical.
Working Principle of Microfiltration System
A microfiltration (MF) system works by passing a liquid through a membrane with micropores (0.1–5.0 µm) that physically block larger particles but allow water and smaller dissolved substances to pass through. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Feed solution Entry – The raw liquid (such as water, milk, fermentation broth, or cell culture medium) is pumped into the MF system.
- Membrane Filtration – The liquid flows across or through the microfiltration membrane. The pore size of the membrane acts like a sieve:
- Retains: suspended solids, bacteria, protozoa, yeast, and particulates.
- Passes through: water, salts, sugars, proteins (depending on size), and other small molecules.
- Retentate & Permeate Streams
- Retentate (concentrate): contains the filtered-out contaminants or biomass.
- Permeate (filtrate): the clarified liquid that passes through the membrane.
- Pressure-Driven Process
- MF works at low pressure (0.1–2 bar) compared to ultrafiltration (UF) or reverse osmosis (RO).
- This makes it energy-efficient and gentle for sensitive products.
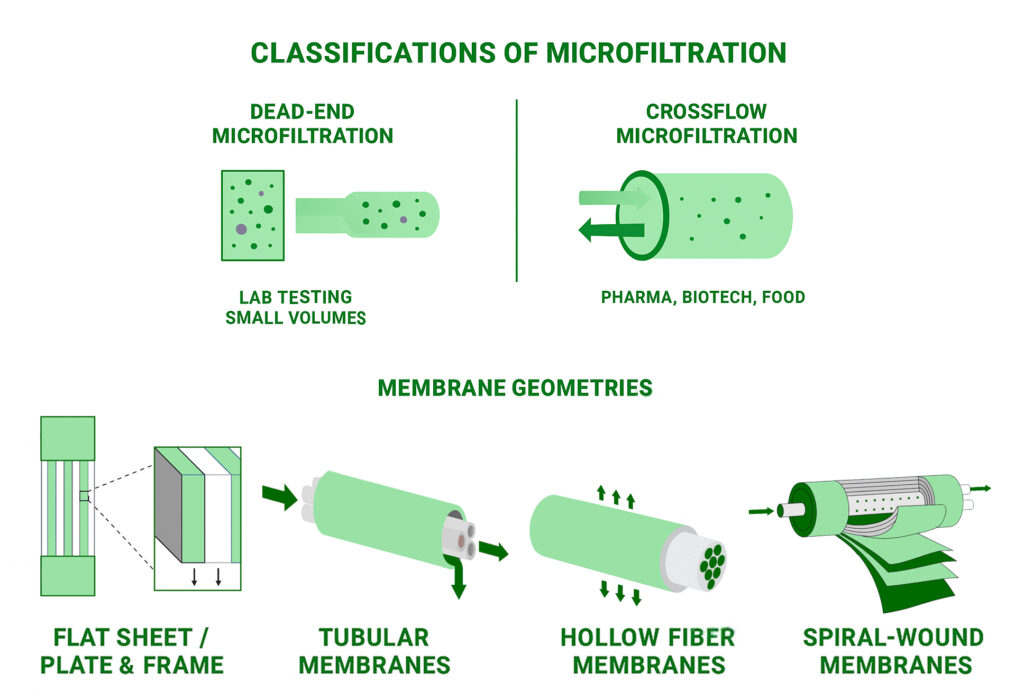
Classifications of Microfiltration
- Based on Flow Configuration
Dead-End Microfiltration
- All feedwater flows perpendicular to the membrane surface.
- Solids accumulate on the membrane surface (cake layer forms).
- Used for low solid loads and smaller volumes.
Crossflow Microfiltration
- Feed flows tangentially across the membrane.
- Helps sweep away retained solids, reducing fouling.
- Common in pharma, biotech, and food applications.
- Based on Membrane Geometry
Flat Sheet / Plate & Frame
- Easy to use in lab-scale systems.
- Good for testing and small-volume applications.
Tubular Membranes
- Large channels for high-solid or viscous fluids (e.g., dairy, wastewater).
- More resistant to fouling.
Hollow Fiber Membranes
- High surface area in compact design.
- Often used for water treatment, sterile filtration, and biopharma.
Spiral-Wound Membranes
- Compact, cost-effective, but less tolerant to high solids.
- Common in food & beverage.
Features of Microfiltration Membrane System

Our system utilizes a specialized membrane with pore sizes typically ranging from 0.1 to 0.6 microns, serving as a physical barrier for particles larger than the pores.

Our system operates with cross-flow or tangential flow filtration, preventing membrane clogging and enhancing filtration efficiency.

The system incorporates pressure control mechanisms, optimizing filtration by maintaining specific pressure differentials across the membrane.

Our modular design ensures flexibility in system configuration, allowing easy scaling based on application requirements. Modules can be added or removed to adjust the system's capacity and accommodate different process needs.
- Precise membrane pore size of 0.1 – 0.6 microns with controlled transmembrane pressure management and cross flow or tangential filtration flow mode of operation ensures maximum filtration efficiency with reduced clogging frequency
- The systems have easily scalable designs to meet varying process requirements by adding or removing modules thus giving advantage for capacity adjustments
- Automated Operations: Integrated controls, sensors, and alarms ensure consistent, efficient filtration performance
- All in one maintenance for peak efficiency operation: multiple cleaning options including chemical cleaning, backwashing, and membrane replacement
- Customization flexibility with tailored features: can help with specific industry-based requirements from pharmaceutical/biopharma validation to food industry sanitary standards
- More than 3.5-decade old experience in making stainless steel grades (SS316, SS316L, SS304) systems: helps in gaining versatility to match application requirements
- Any standard makes membrane compatibility in terms of fittings: support for various materials including ceramic and polymeric options like PVDF
- Intelligent Monitoring: Real-time tracking of critical parameters including temperature, pressure, flow rate, pH, and conductivity
- Space-Efficient Design: Compact systems suitable for both laboratory and large-scale industrial applications
Applications of Microfiltration Membrane Systems in different Industries
Pharmaceutical
| purification, concentration, and particle removal from API, small molecules, etc. |
Biotechnology/Biopharmaceutical
| sterile filtration, protein harvesting, cell separation and fermentation broth clarification |
Dairy
| milk standardization, bacterial removal and improved product safety, whey processing, etc. |
Food and Beverages
| clarification of juices, sauces, wines, beers, and dairy products for enhanced stability and extended shelf life |
Electronics
| process fluid purification |
Food and Beverages | clarification of juices, sauces, wines, beers, and dairy products for enhanced stability and extended shelf life |
Pharmaceutical | purification, concentration, and particle removal from API, small molecules, etc. |
Biotechnology/Biopharmaceutical | sterile filtration, protein harvesting, cell separation and fermentation broth clarification |
Dairy | milk standardization, bacterial removal and improved product safety, whey processing, etc. |
Electronics | process fluid purification |
A GLIMPSE OF THIS PRODUCT
Watch Microfiltration Systems in 360°
Rotate the product using mouse to experience product in 360°
FAQs
Microfiltration membrane system is a system used for clarification of solutions towards microbial biomass and colloidal particles separation. It uses a semipermeable membrane having pore size varying from 0.1-10 microns. It finds application in a variety of industries food and beverages, fermentation broth i.e. industrial biotech, nutraceuticals, biopharma, pharma, etc.
A microfiltration (MF) system works by passing a liquid through a membrane with micropores (0.1–10.0 µm) that physically block larger particles but allow water and smaller dissolved substances to pass through. It’s a pressure driven process working on cross flow filtration mode.
Microfiltration (MF) can be classified in different ways depending on flow configuration (dead end MF and cross flow MF), membrane type (tubular, spiral, hollowfibre ), and application (Sterile Filtration (0.22 µm–0.45 µm), Clarification (0.45 µm–1.0 µm), Biomass Concentration (0.1 µm–0.5 µm), Pretreatment for UF/NF/RO)
MF → removes particles & bacteria
UF → removes proteins & viruses
NF → removes salts & organics
RO → removes all dissolved substances (highest purity)
1. Microfiltration (MF) - Pore size: ~0.1 – 5.0 µm - removes suspended solids, bacteria, yeast, some large colloids.
2. Ultrafiltration (UF) - Pore size / MWCO: 1,000 – 800,000 Daltons – removes viruses, proteins, colloids, macromolecules.
3. Nanofiltration (NF) - Pore size / MWCO: 200 – 1,000 Daltons - removes: divalent & multivalent salts, organic molecules, pesticides.
4. Reverse Osmosis (RO) - Pore size: < 100 Daltons - removes: Nearly all dissolved salts, ions, organics, and impurities.
The principle of a microfiltration (MF) unit is based on physical separation by size exclusion using a semi-permeable membrane with a driving force which is a simple transmembrane pressure (TMP) applied by a pump.