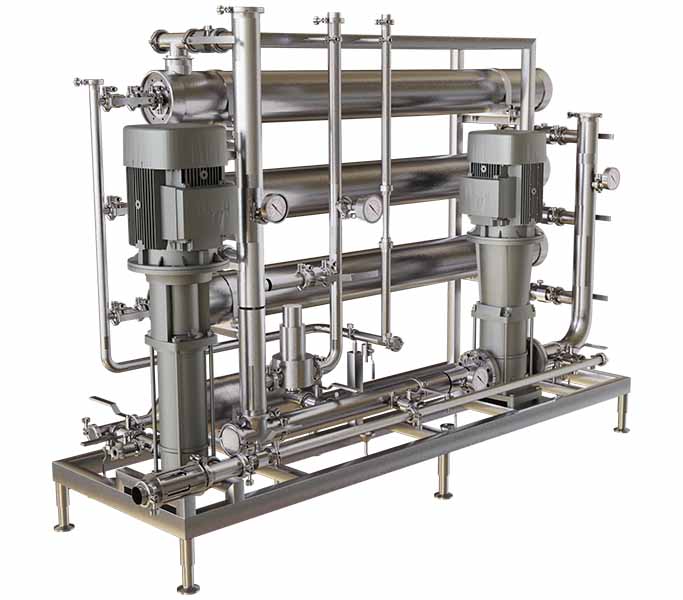
Membrane Systems
Reverse Osmosis System
Sanitech Engineers, among the trusted reverse osmosis system manufacturers, develops state-of-the-art reverse osmosis membrane solutions with systems meeting all international regulatory standards.
The ultimate step in the membrane filtration spectrum is to recover water, and thus the tightest membrane is chosen which can reject the smallest of the particles. None other than the Reverse Osmosis System (RO) is the only chosen membrane-based filtration technology option used across diverse industries for water recovery. Like other membranes, it also uses a semi-permeable membrane with extremely fine pores to separate contaminants and solutes from solvents.
Since it is the tightest membrane of all, by applying pressure, water molecules are forced to pass into permeate against the osmotic pressure. Hence, it is the most energy-consuming activity but gives an opportunity to recover reusable water from any stream. It does have limitations of COD, BOD, silica, and conductivity, but by bringing these parameters in range, the solution can surely be processed. This makes the reverse osmosis system commercial applications highly valuable in industries like food processing, pharma, and chemicals.
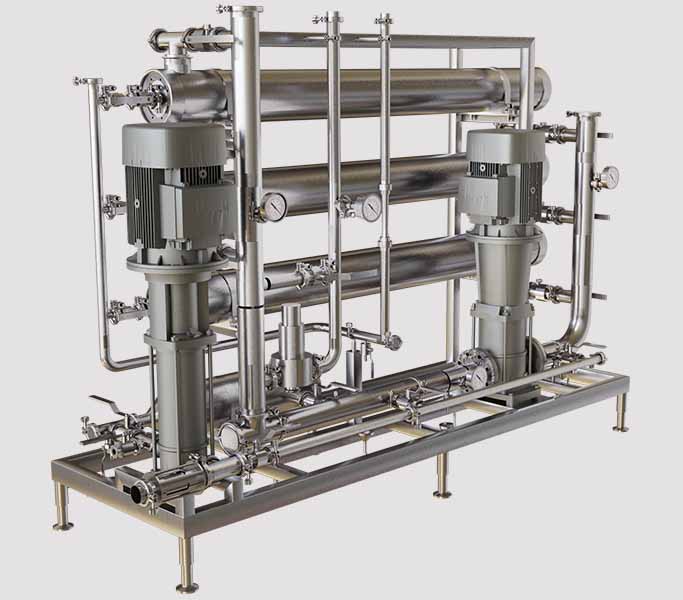

Understanding Reverse Osmosis : Working Principle and Types
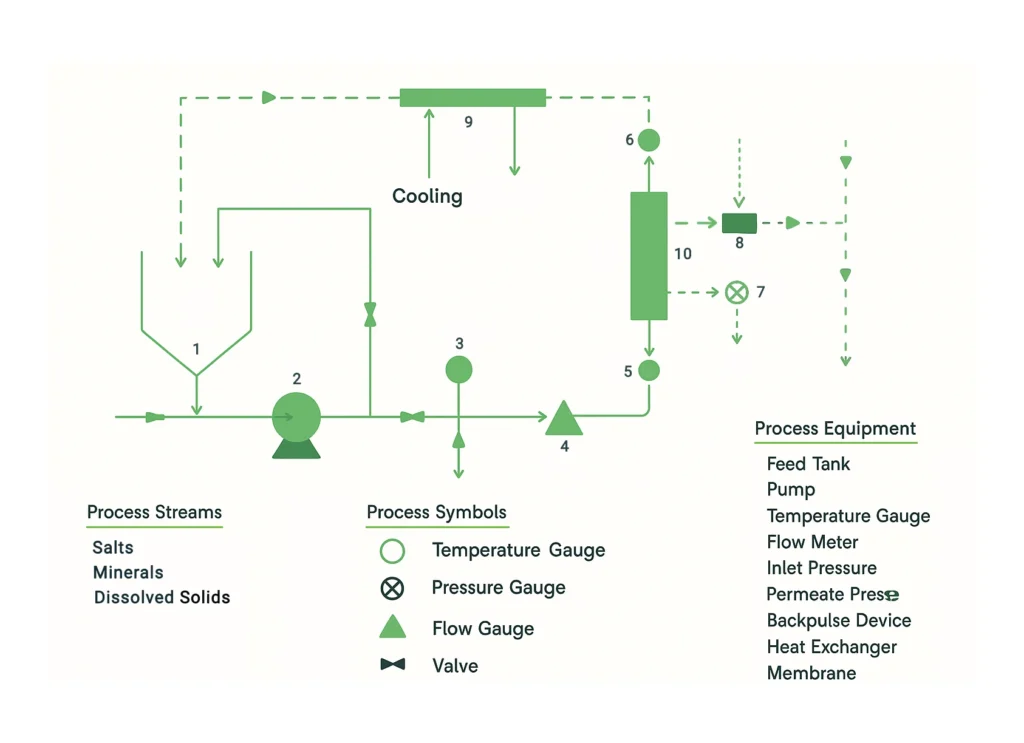
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a high-pressure membrane separation process that removes dissolved salts, organic molecules, and impurities at the ionic level. RO membranes have a pore size of ~0.1–1 nm and a MWCO below 200 Daltons.
Working Principle of Reverse Osmosis System
High pressure forces liquid through semi-permeable membranes (~0.1–1 nm), removing dissolved salts and impurities.
- Feed Solution Entry – High pressure is applied to push the liquid against the RO membrane.
- Membrane Separation – The semi-permeable membrane blocks salts and dissolved solids while allowing only solvent molecules to pass.
- Retentate & Permeate – Retentate is the concentrated brine/reject, permeate is the purified solvent.
- Operating Pressure – Works typically at 10–80 bar depending on feed concentration.
Classifications of Reverse Osmosis
- Membrane Types – Thin-film composite (TFC), cellulose acetate.
- Designs – Spiral wound, hollow fiber.
- Operating Range – Low-pressure RO, brackish water RO, high-pressure RO.
System Components and Features of Reverse Osmosis System:
- High-Performance precise membrane pore size of < 100 Da with controlled transmembrane pressure management and cross flow or tangential filtration flow mode of operation ensures maximum filtration efficiency with careful separation control. This is critical for any reverse osmosis system industrial application requiring high purity levels.
- Thin-film composite material: polyamide and specialized polymeric materials with ultra-fine pores rejecting contaminants and dissolved solids.
- Precision Pressure Systems: Integrated pressure pumps generate the necessary hydraulic pressure to overcome osmotic pressure and drive efficient separation.
- Optional integration with pre-treatment processes: our microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and nanofiltration systems provide ideal upstream filtration for a reverse osmosis system water filter setup.
- Uniform hydraulic pressure distribution: engineered pressure vessels with robust housing ensure consistent and uniform pressure across membrane surface.
- Dual Stream Output: Process generates two distinct streams – purified permeate water and concentrated reject stream containing filtered impurities, both carefully separated and collected.
- Advanced Flow Control: Precise flow control mechanisms maintain steady feed water and permeate flow rates for reliable system performance.
- Advanced control systems: intelligent automation to monitor and adjust operating parameters for consistent, efficient performance.
- Compact systems with versatile design: scalable from laboratory research to full reverse osmosis system industrial production setups.
- Dedicated clean-in-place systems: integrated for ensuring long-term performance.
- Advanced sensors and alarm systems: real-time detection of potential issues and deviations from optimal operating conditions.
Key Applications of RO System:
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
| Production of purified water for pharmaceutical processes and Water for Injection (WFI) applications
|
Nanomaterials
| Nanoparticle concentration in advanced synthesis processes
|
Desalination
| Essential technology generating potable water from seawater and brackish water
|
Industrial Water Production
| Generating ultra-pure water
|
Food & Beverage Processing
| beverage concentration
|
Recovery
| valuable component recovery from industrial effluents, efficient water recovery from various industrial process streams
|
Recovery
| acid and caustic concentration and separation for reuse
|
Desalination | Essential technology generating potable water from seawater and brackish water |
Industrial Water Production | Generating ultra-pure water |
Food & Beverage Processing | beverage concentration |
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Production of purified water for pharmaceutical processes and Water for Injection (WFI) applications |
Recovery | valuable component recovery from industrial effluents, efficient water recovery from various industrial process streams |
Nanomaterials | Nanoparticle concentration in advanced synthesis processes |
Recovery | acid and caustic concentration and separation for reuse |
A GLIMPSE OF THIS PRODUCT
Watch Reverse Osmosis System In 360°
Rotate the product using mouse to experience product in 360°
FAQs
An industrial reverse osmosis (RO) system is a pressure-driven membrane filtration technology used to separate water and low-molecular-weight solutes from valuable products. In product processing, RO works by forcing liquid feed through semi-permeable membranes that retain larger molecules (like sugars, proteins, nutraceuticals, salts or bioactive compounds) while allowing water to pass through.
This makes it highly useful for concentrating products (juices, dairy whey, herbal extracts), improving purity, and reducing downstream drying costs.
Industrial reverse osmosis (RO) is used in product processing to concentrate, purify, and recover valuable compounds without heat damage. It is widely applied in dairy (whey protein, lactose reduction), food & beverages (juice, coffee, sugar), pharma & biotech (enzymes, antibiotics, biomolecules), and nutraceuticals (plant extracts, proteins). RO enables high product quality and cost savings by preserving sensitive ingredients while reducing energy use.
Commercially, osmosis, specifically reverse osmosis (RO) is used to separate water from dissolved salts and impurities, or to concentrate valuable products. In industries, this process is applied to purify water for pharma & biotech, concentrate dairy proteins, clarify juices, improve beverage taste, and recover high-value nutraceuticals, all without heat damage, ensuring better quality and efficiency.
Reverse osmosis (RO) in industry is applied for product purification, concentration, and desalting. It is widely used in pharmaceuticals and biotech for ultrapure process water, in dairy for whey protein concentration, in food & beverages for juice clarification and flavor enhancement, and in nutraceuticals for gentle extraction and concentration of actives.
Reverse osmosis can be considered eco-friendly in product processing because it uses membrane separation without harsh chemicals, preserves heat-sensitive compounds, and reduces the need for energy-intensive evaporation. However, its eco-impact depends on energy use and concentrate (reject) disposal industries that recycle or valorize the concentrate make RO much more sustainable.

